1. Voluntary Turnover: This occurs when employees choose to leave the organization on their own accord. Reasons for voluntary turnover can vary widely, including better career opportunities, dissatisfaction with the work environment, or personal reasons.
2. Involuntary Turnover: In contrast to voluntary turnover, involuntary turnover happens when employees are terminated or laid off by the organization. This could be due to poor performance, restructuring, or other business-related reasons.
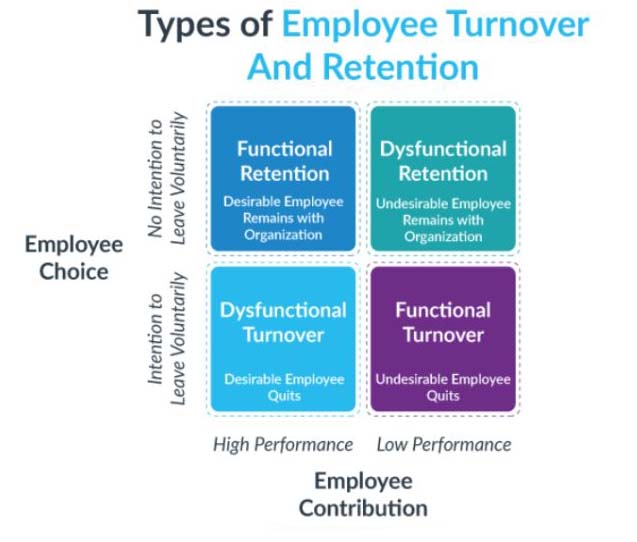
3. Functional Turnover: Functional turnover occurs when low-performing employees voluntarily leave the organization. While this type of turnover might initially seem positive, as it removes underperformers, it can also indicate deeper issues within the organization, such as poor management or lack of career development opportunities.
4. Dysfunctional Turnover: Dysfunctional turnover refers to the departure of high-performing or valuable employees. This type of turnover can be particularly detrimental to an organization, as it results in the loss of top talent and institutional knowledge.
5. Controllable Turnover: Controllable turnover occurs when factors contributing to employee departure are within the organization’s control. This could include issues such as poor management, lack of career growth opportunities, or inadequate compensation.
6. Uncontrollable Turnover: Uncontrollable turnover, on the other hand, is influenced by external factors beyond the organization’s control, such as retirement, relocation, or changes in personal circumstances.
To make your recruitment job easier, try epicareer.com/employer . It is a platform that connects recruiters with qualified candidates. It’s a great way to find the perfect candidates for your open positions, and it can save you a lot of time and hassle.
With Epi Career for Employer, you can:
– Access a large database of qualified candidates
– Post your open positions and start receiving candidates immediately
– Get in touch with candidates directly

 Follow
Follow